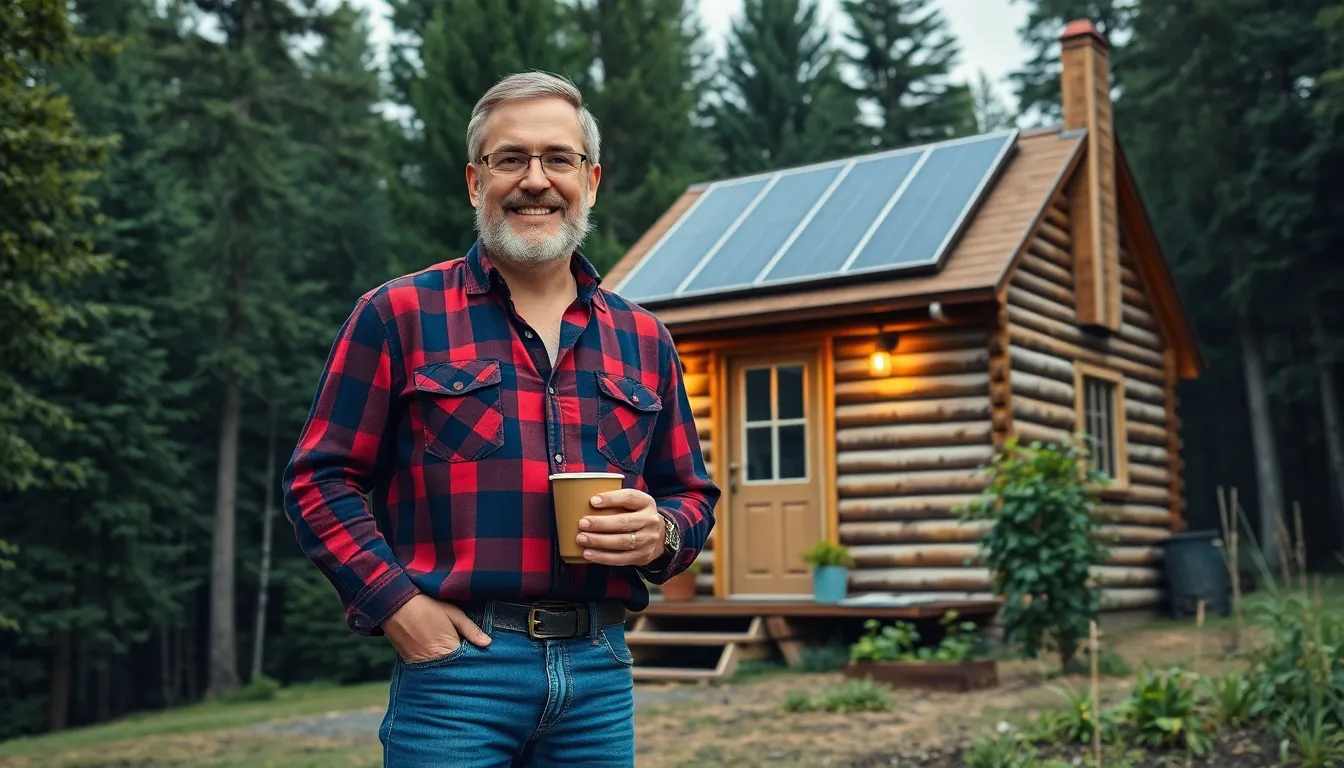
Imagine waking up to the sound of chirping birds instead of blaring alarms, sipping coffee brewed over a crackling fire instead of a buzzing kettle. Living off the grid isn’t just an escape; it’s an adventure that promises freedom from the daily grind and a chance to reconnect with nature. It’s about trading in Wi-Fi for wilderness and city noise for the soothing rustle of leaves.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Living Off The Grid
Living off the grid represents a lifestyle choice that prioritizes self-sufficiency and a close connection to nature. This approach empowers individuals to break away from conventional living.
Definition of Off-Grid Living
Off-grid living involves residing in a manner that does not rely on public utilities for essential services such as electricity, water, and sewage. Self-sufficient setups often include solar panels, wind turbines, and rainwater collection systems. Housing choices vary from tiny homes to cabins, designed to minimize environmental impact. Off-grid living promotes environmental sustainability, allowing people to be more attuned to their surroundings.
The Benefits of Going Off-Grid
Going off-grid offers multiple advantages that enhance personal well-being. Freedom from utility bills reduces financial stress and leads to potential savings. Many enjoy increased privacy and solitude, appreciating the peace outside urban noise. Enhanced physical health often results from outdoor activities, boosting mental clarity and emotional resilience. Additionally, individuals cultivate essential skills in areas such as food production through gardening, contributing to personal fulfillment.
Essential Components of Off-Grid Living
Living off the grid requires careful planning and implementation of essential components that ensure sustainability and self-sufficiency.
Energy Sources
Solar panels supply a popular energy source for off-grid living. They convert sunlight into electricity, offering a renewable and consistent power option. Wind turbines also contribute, harnessing wind energy to generate electricity. Battery storage systems store excess energy, providing power during low generation periods. Biogas systems utilize organic waste to produce energy, addressing waste management issues while generating power. Each energy source plays a crucial role, creating a reliable setup for off-grid homes.
Water Supply
Rainwater harvesting systems collect and store rainwater for multiple uses. This method offers a sustainable and efficient approach, especially in areas with sufficient rainfall. Well systems provide an alternative water source by tapping into underground aquifers. Water filtration systems ensure clean drinking water by removing impurities and contaminants. Additionally, greywater systems recycle water from sinks and showers for irrigation, reducing overall water consumption. Effective management of water resources is vital for successful off-grid living.
Waste Management
Composting toilets serve as a key element in off-grid waste management. These toilets convert human waste into compost, eliminating the need for traditional plumbing. Anaerobic digesters also break down organic waste, producing biogas for energy while reducing landfill contributions. Recycling practices, such as separating paper, plastic, and metal, minimize waste production and promote sustainability. Creating designated waste disposal systems helps maintain hygiene and environmental balance. Efficient waste management contributes significantly to an off-grid lifestyle.
Preparing for the Transition
Preparing for off-grid living involves thoughtful planning and a clear vision. Various aspects require consideration to ensure a successful shift to this lifestyle.
Choosing the Right Location
Vacant land in rural areas often suits off-grid living best. Accessibility to natural resources like water and sunlight plays a crucial role. Proximity to local towns helps access essential supplies without sacrificing solitude. Wildlife presence can enhance the experience, but nearby neighbors lessen extreme isolation. Researching local regulations ensures compliance and avoids future complications.
Building or Buying an Off-Grid Home
Multiple options exist for acquiring an off-grid home. Building a custom home allows complete control over design and features. Prefabricated homes offer a faster, often more cost-effective solution. Alternative structures, like tiny homes or earth-sheltered buildings, enhance energy efficiency. Each choice depends on budgets, timelines, and personal preferences. Evaluating the pros and cons ensures informed decisions about housing that meets off-grid needs.
Challenges of Living Off The Grid
Living off the grid presents unique challenges that require careful consideration and planning. It’s essential to address various hurdles to ensure a successful transition.
Legal and Regulatory Issues
Navigating legal and regulatory issues often complicates off-grid living. Local building codes may impose restrictions on structures without access to traditional utilities. Zoning laws can affect land usage and what residents can build. Permits might be necessary for rainwater collection systems or solar panel installations. Understanding local regulations can prevent significant setbacks. Overlooking these requirements could result in fines or mandatory alterations.
Sustaining a Reliable Food Supply
Sustaining a reliable food supply poses its own set of challenges. Establishing food production through gardening requires knowledge of local climates and soil conditions. Crop selection must align with the growing season and available resources. Additionally, alternative practices like foraging and hunting depend on environmental awareness. Skills in food preservation, such as canning or dehydrating, enhance independence. Without these methods, food security may become an issue for off-grid individuals.
Embracing an off-grid lifestyle offers an enriching way to reconnect with nature and achieve self-sufficiency. By stepping away from the demands of modern living individuals can cultivate a deeper appreciation for their surroundings and develop essential skills that enhance personal fulfillment.
While challenges exist in transitioning to this lifestyle careful planning and research can pave the way for a successful off-grid experience. With the right resources and mindset anyone can enjoy the benefits of living off the grid while contributing positively to the environment.
Ultimately this journey is about finding balance and peace in a simpler way of life.




